e-business
Many firms now see developing e-business as a key part of their business strategy.
Definitions
E-commerce is described as 'all electronically mediated information exchanges between an organisation and its external stakeholders'. An e-commerce transaction can thus be considered from two perspectives.
E-business has been defined as the transformation of key business processes through the use of internet technologies.
So, e-commerce is a subset of e-business. The most generic description of e-commerce is trading on the internet, buying and selling products and services online.
Porter
Porter suggested three ways in which IS/IT in general can affect the competitive environment and an organisation's ability to compete.Though these points apply to IS/IT in general, they are particularly important when considering e-business.
- New businesses might become possible. For example, auction sites and photo-album sites.
- The industry structure can be changed. For example, in the music business it can be argued that the large CD publishers have less power because music can be self-published on the internet.
- IS/IT can provide an organisation with competitive advantage by providing new ways of operating. For example, airlines save money by encouraging internet bookings.
Different types of e-business
Categories of e-business
The categories of e-business functions are shown below:
- B2B (business to business). For example, a supermarket IS system automatically placing orders into suppliers' IS systems.
- B2C (business to consumer). Selling over the internet - books, flights, music, etc.
- C2B (consumer to business). Some internet sites display a selection of suppliers' offerings from which the user can choose. A model that largely depends on the internet.
- C2C (consumer to consumer). Auction sites, such as ebay, putting consumers in touch with each other. Amazon does the same by offering second-hand books. This model largely depends on the internet.
- 'Buy side' e-commerce focuses on transactions between a purchasing organisation and its suppliers.
- 'Sell side' e-commerce focuses on transactions between a purchasing organisation and its customers.
The stages of e-business
The stages of e-business can be described as:
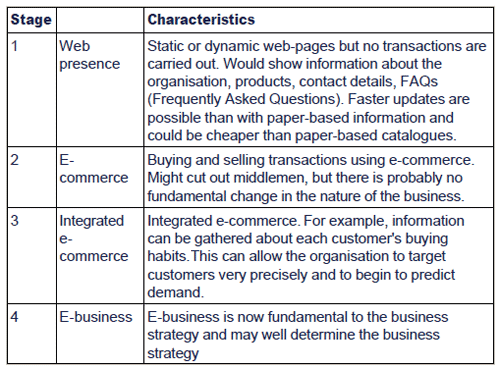
This model helps businesses to understand where they are in the process of e-business, and this will help them to decide where to go next with further development.
Pros and cons of e-business
Benefits of e-business
Most companies employ e-business to achieve the following:
- Cost reduction - e.g. lower overheads, cheaper procurement
- Increased revenue - e.g. online sales, better CRM
- Better information for control - e.g. monitoring website sales
- Increased visibility
- Enhanced customer service - e.g. via extranets
- Improved marketing - e.g. e-mailing customers with special offers
- Market penetration - e.g. even small suppliers can gain a global presence via the internet
- The combination of the above should be to enhance the company's competitive advantage
Barriers to e-business
Barriers to e-business can be seen in both the organisation itself and in its suppliers and customers. They include:
- Technophobia. Senior managers are distrustful and sceptical about the alleged benefits of e-business
- Security concerns about hackers and electronic fraud
- Set-up costs. Simple, static pages are cheap to set up, but dynamic pages, linking to e-commerce systems and databases, with impressive design values are expensive to set up
- Running costs. Renting space on a web-server. Also, maintenance of websites is very important as most users are very unforgiving about out-of-date sites. Updating, say with special offers, is also needed to encourage return visits, perhaps linked to email campaigns
- Limited opportunities to exploit e-business. Some businesses (such as selling books) are more suitable for e-business than others (such as selling carpets)
- Limited IT resources in house (e.g. a lack of staff skills creating staff resistance) so recruitment is needed or all development and maintenance has to be sub-contracted
- Customers not likely to be interested in e-business (e.g. firms targeting retired pensioners).
Further detail
Two key areas where IT/IS have impacted firms are supply chain management and customer relationship management. Click on the above links to explore these concepts in more detail.
|
Created at 10/10/2012 10:57 AM by System Account
(GMT) Greenwich Mean Time : Dublin, Edinburgh, Lisbon, London
|
Last modified at 9/11/2013 12:21 PM by System Account
(GMT) Greenwich Mean Time : Dublin, Edinburgh, Lisbon, London
|
|
|
|
 |
Rating
:
|
 Ratings & Comments
(Click the stars to rate the page) Ratings & Comments
(Click the stars to rate the page)
|
 |
Tags:
|
|