Economic Value Added (EVA)
EVA is a performance management measure developed by Stern Stewart and Co.
What is EVA?
The most common objective in decision making scenarios is to maximise shareholder value. This is because most decisions are made by companies where the directors have a duty to act in the interests of their shareholders.
Research has found that to develop decision making metrics that maximise shareholder value, the following factors need to be incorporated:
1 Cash is preferable to profit
Cash flows have a higher correlation with shareholder wealth than profits.
2 Exceeding the cost of capital
The return, however measured, must be sufficient to cover not just the cost of debt (for example by exceeding interest payments), but also the cost of equity.
Peter Drucker commented, in a Harvard Business Review article: ‘Until a business returns a profit that is greater than its cost of capital, it operates at a loss. Never mind that it pays taxes as if it had a genuine profit. The enterprise still returns less to the economy than it devours in resources… until then it does not create wealth; it destroys it.’
3 Managing both long and short-term perspectives
Investors are increasingly looking at long-term value. When valuing a company’s shares, the stock market places a value on the company’s future potential, not just its current profit levels.
EVA is an attempt to address the above three issues.
EVATM is a measure of performance similar to residual income, except the profit figure used is ECONOMIC profit and the capital employed figure used is ECONOMIC capital employed. It is argued that the profit and capital employed figures quoted in the financial statements do not give the true picture and that the accounting figures need to be adjusted to show the true underlying performance.
The basic concept of EVA is that performance should be measured in terms of the value added during the period. It is a measure of performance that is directly linked to shareholder wealth.
Basic calculation

Decision rule: accept the project if the EVA is positive.
What is NOPAT?

Adjustments to PAT

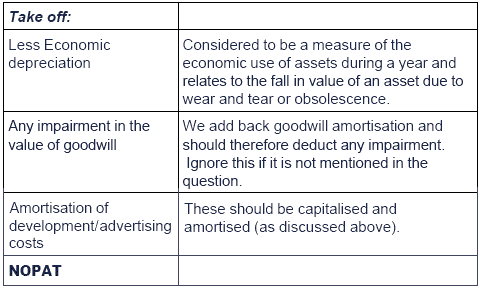
What is the economic value of capital employed?
The main adjustments to the capital employed figure are as follows:
- an adjustment should be made to reflect the replacement cost of non-current assets rather than the book value.
- the net book value of any capitalised operating leases should be added back.
- the net book value of any capitalised development/advertising costs should be added back.
- the value of amortised goodwill should be added.
What is the WACC?
WACC stands for weighted average cost of capital:
WACC = (proportion of equity × cost of equity) + (proportion of debt × post tax cost of debt)
For example suppose that a company is 60% financed by equity which has a cost of 10% pa and 40% financed by debt which has an after tax cost of 6%
WACC = (0.60 x 0.10) + (0.40 x 0.06) = 0.084 therefore 8.4%
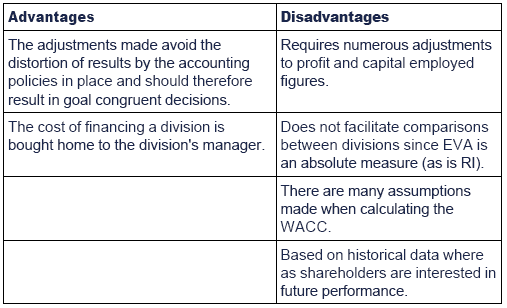
Advantages and disadvantages of EVA
|
Created at 6/6/2012 10:10 AM by System Account
(GMT) Greenwich Mean Time : Dublin, Edinburgh, Lisbon, London
|
Last modified at 10/10/2013 4:34 PM by System Account
(GMT) Greenwich Mean Time : Dublin, Edinburgh, Lisbon, London
|
|
|
|
 |
Rating
:
|
 Ratings & Comments
(Click the stars to rate the page) Ratings & Comments
(Click the stars to rate the page)
|
 |
Tags:
|
|
|
|
|