Activity Based Budgeting
Activity based budgeting is one approach to budgeting that relies on cost drivers and is closely related to activity based costing.
Definition
ABB is defined as: 'a method of budgeting based on an activity framework and utilising cost driver data in the budget-setting and variance feedback processes'.
Or, put more simply, preparing budgets using overhead costs from activity based costing methodology.
Advantages and disadvantages of ABB
Advantages
The advantages of ABB are similar to those provided by activity-based costing (ABC).
- It draws attention to the costs of 'overhead activities' which can be a large proportion of total operating costs.
- It recognises that it is activities which drive costs. If we can control the causes (drivers) of costs, then costs should be better managed and understood.
- ABB can provide useful information in a total quality management (TQM) environment, by relating the cost of an activity to the level of service provided.
Disadvantages of ABB
- A considerable amount of time and effort might be needed to establish the key activities and their cost drivers.
- It may be difficult to identify clear individual responsibilities for activities.
- It could be argued that in the short-term many overhead costs are not controllable and do not vary directly with changes in the volume of activity for the cost driver. The only cost variances to report would be fixed overhead expenditure variances for each activity.
The activity matrix
An activity-based budget can be constructed by preparing an activity matrix. This identifies the activities in each column, and the resources required to carry out the activities in each row.
The following 'activity matrix' shows the resources used (rows) and major functions/activities (columns) of a stores department. In this example, all the identified activities occur within a single department.
- The total current annual costs of each resource consumed by the department are shown in the final column; they have then been spread back over the various activities to establish the cost pools. The allocation of resource costs between activities will, to some extent, be subjective.
- Each of the first four activities has an identifiable cost driver, and the total resource cost driver rates can be determined (cost per unit of activity).
- The last two activities that occur within the department are non-volume related, and are sometimes referred to as 'sustaining costs'. They are necessary functions and should not be ignored in the budgeting process; however, they should not be attributed to particular cost drivers, as this would not reflect their true cost behaviour and would result in inappropriate budgets being set.
Activity cost matrix for stores department
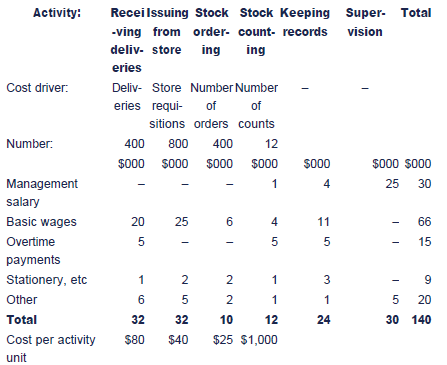
Sustaining costs will effectively be treated as fixed costs. However, for control purposes, activity-based costs can be assumed to be variable, and actual costs can be compared with the expected costs for the given level of activity.
Your FeedbackWe value your feedback on the topics or anything else you have found on our site, so we can make it even better.Give Feedback
|
Created at 6/7/2012 4:33 PM by System Account
(GMT) Greenwich Mean Time : Dublin, Edinburgh, Lisbon, London
|
Last modified at 11/1/2016 4:22 PM by System Account
(GMT) Greenwich Mean Time : Dublin, Edinburgh, Lisbon, London
|
|
|
|
 |
Rating
:
|
 Ratings & Comments
(Click the stars to rate the page) Ratings & Comments
(Click the stars to rate the page)
|
 |
Tags:
|
|
|
|
|